Overview
The robotis_manipulator package is a library package for controlling the manipulator. This package provides a manipulator class for setting manipulator parameters, and provides some math functions to configure the manipulator controller and a basic trajectory generators that uses minimum jerk. The user makes a class inheriting RobotisManipulator class, and set up the class by using the provided functions and the vurtual classes. The class provides functions such as creating the trajectory, receiving joint positions from the actuators and sending the target positions to the actuators. The open_manipulator_libs package can be refer as an example.
Installation
The robotis_manipulator package is supported in ROS and OpenCR environments. User can write own program to control user’s manipulators by using the robotis_manipulator package on ROS environment. If you want to use robotis_manipulator in a more simple development environment, you can use OpenCR, one of the powerful embedded systems. Users can easily take robotis_manipulator in arduino IDE environment that supports OpenCR.
ROS Package
NOTE : The test is done on ROS Kinetic Kame installed in Ubuntu 16.04.
Install Ubuntu on PC
Download and install Ubuntu 16.04 on your PC.
If you need more help with installing Ubuntu, check out the step-by-step guide from the link below.
Install ROS on PC

The following script will allow you to simplify the ROS installation procedure. Run the following command in a terminal window. The terminal application can be found with the Ubuntu search icon on the top left corner of the screen. The shortcut key to open a terminal is Ctrl+Alt+t. After installing ROS, please reboot PC.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/robotis_tools/master/install_ros_kinetic.sh && chmod 755 ./install_ros_kinetic.sh && bash ./install_ros_kinetic.sh
NOTE: In order to check which packages are installed, please check this link out. install_ros_kinetic.sh
If you prefer manual installation, please following the link below.
Install ROS Package
Install the robotis_manipulator package. Run the following command in a terminal window.
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src/
$ git clone https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/robotis_manipulator.git
$ cd ~/catkin_ws && catkin_make
If the catkin_make command has been completed without any errors, all the preparations for using the robotis_manipulator package are done.
OpenCR
Connection
Connect PC and OpenCR to micro USB as shown below.

NOTE : Please refer the detailed description of OpenCR.
Arduino IDE Setup
NOTE: This page only explain the setup process of OpenCR of the linux envirnment. If you want to use OpenCR in windows or mac environments, please refer to Arduino IDE for using OpenCR.
Install Arduino IDE(Linux)
Download the latest version of Arduino IDE from the official arduino homepage, and install it. Currently, the OpenCR will be on service in the version 1.6.4 or later.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
Then, extract the downloaded file to the desired folder and execute the installation file from the terminal. In this case, the example shown below makes the folder tools in the user’s top folder (~/). This folder will act as the Arduino IDE folder.
$ cd ~/tools/arduino-1.6.4
$ ./install.sh
Set the file path of installed Arduino IDE as an absolute path named PATH in the bashrc file. Here recommends to use gedit editor. (Use another editor, if necessary.) Finally, source it to apply the changes.
$ gedit ~/.bashrc
$ export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/tools/arduino-1.6.4
$ source ~/.bashrc
Run Arduino IDE(Linux)
To run the Arduino IDE on Linux platform, type into the terminal as follows.
$ arduino
Porting to Arduino IDE(Linux)
Preferences
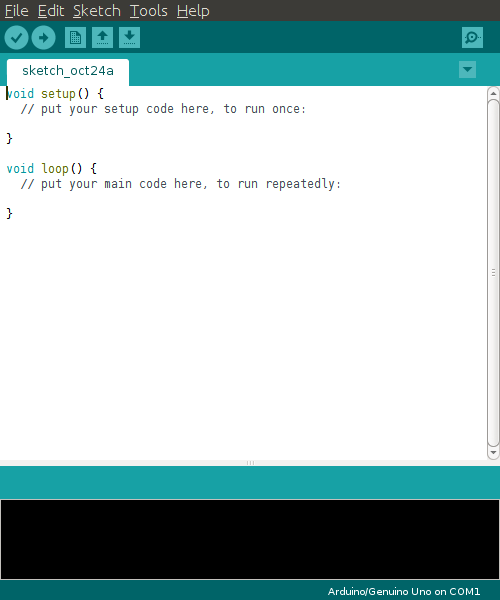
After Arduino IDE is run, click File → Preferences in the top menu of the IDE. When the Preferences window appears, copy and paste following link to the Additional Boards Manager URLs textbox. (This step may take about 20 min.)
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/OpenCR/master/arduino/opencr_release/package_opencr_index.json
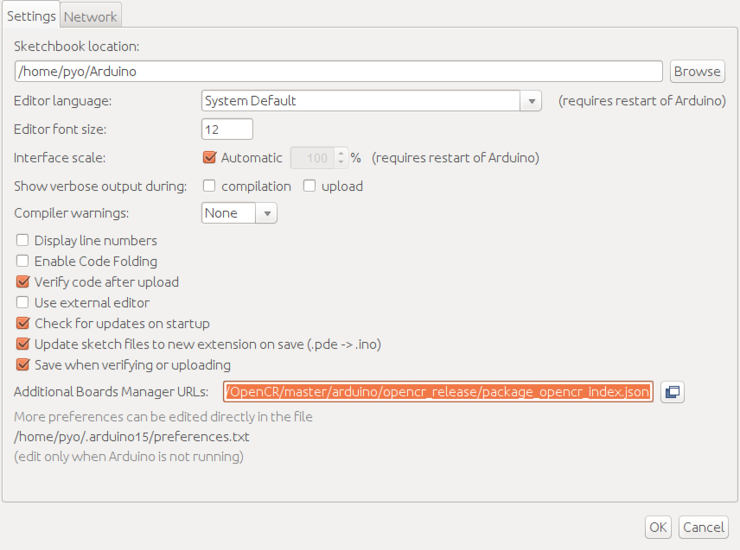
Install the OpenCR package via Boards Manager
Click Tools → Board → Boards Manager.
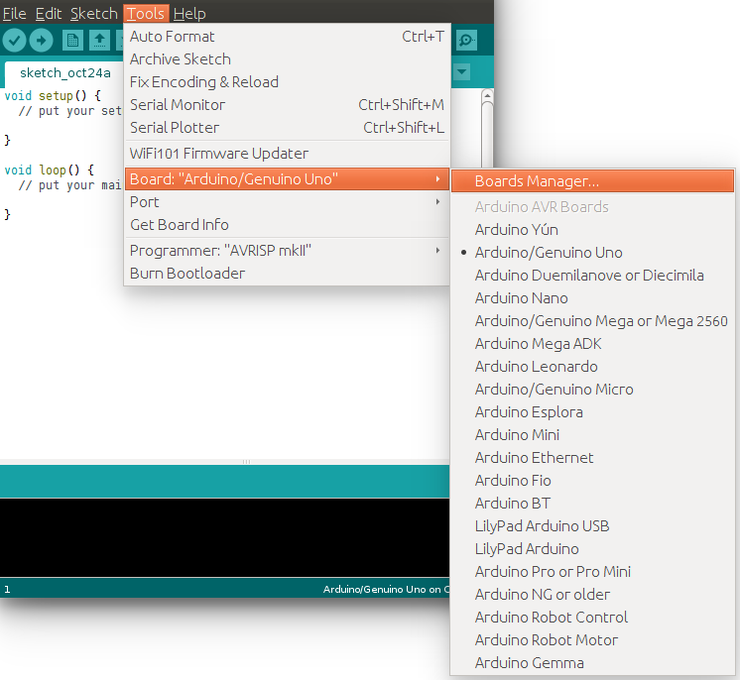
Type OpenCR into the textbox to find the OpenCR by ROBOTIS package. After it finds out, click Install.
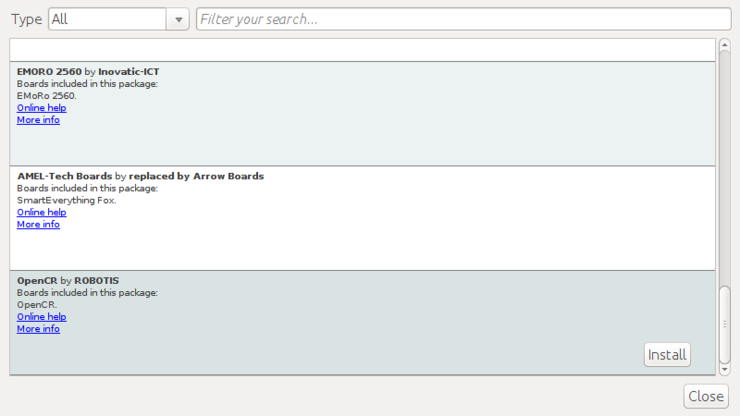
After the installation, “INSTALLED” will be appeared.
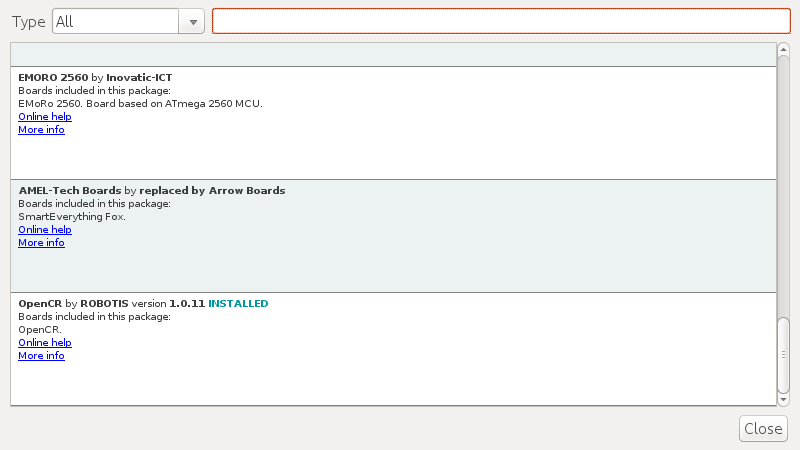
See if OpenCR Board is now on the list of Tools → Board. Click this to import the OpenCR Board source.

Port setting
This step shows the port setting for the program uploads. The OpenCR should be connected to the PC and the OpenCR via the USB ports.
Select Tools → Port → /dev/ttyACM0.
WARNING : The last digit value 0 in the string /dev/ttyACM0 might be different depend on the USB connection environment.
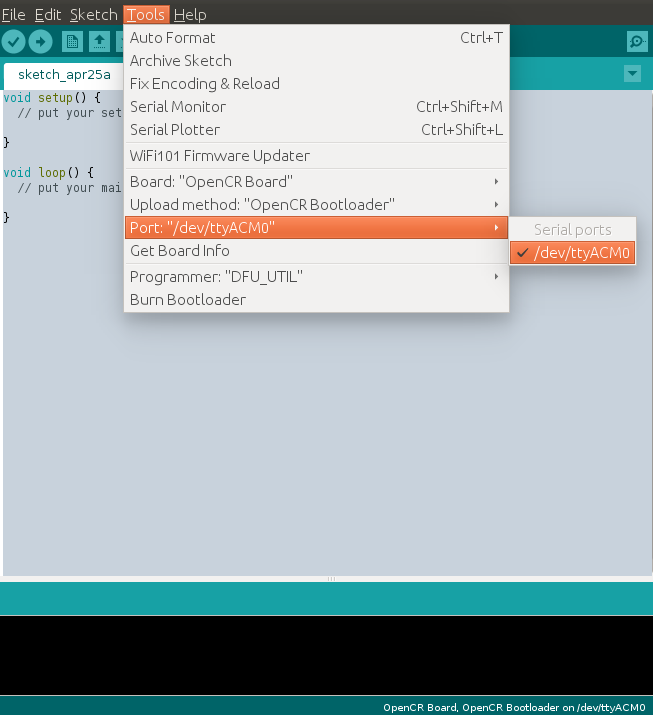
NOTE: Please refer to Arduino IDE for using OpenCR(linux) for detailed setting method.
API References
Click here to open the API Reference manual
Usage Tutorials
The robotis_manipulator is a library that stores parameters needed to control a manipulator, and performs kinematics solving, trajectory generation, and actuator communication. This tutorial describes how to use the robotis_manipulator.
In this tutorial, we will use open_manipulator_libs created to control OpenMANIPULATOR-X RM-X52-TNM, as an example.
Step1 Make Manipulator Class
#define CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_SIZE 4
class OpenManipulator : public robotis_manipulator::RobotisManipulator
{
private:
robotis_manipulator::Kinematics *kinematics_;
robotis_manipulator::JointActuator *actuator_;
robotis_manipulator::ToolActuator *tool_;
robotis_manipulator::CustomTaskTrajectory *custom_trajectory_[CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_SIZE];
public:
OpenManipulator();
virtual ~OpenManipulator();
void initOpenManipulator(bool using_actual_robot_state, STRING usb_port = "/dev/ttyUSB0", STRING baud_rate = "1000000", float control_loop_time = 0.010);
void processOpenManipulator(double present_time);
};
Create a manipulator class that inherits the robotis_manipulator::RobotisManipulator class.
In this example, we created initOpenManipulator and processOpenManipulator as public functions of the class.
Step2 Initialize Manipulator
The InitOpenManipulator function sets the manipulator DH (Denavit-Hartenberg) parameters, kinematics solver, actuator, and trajectory generators.
Below is the InitOpenManipulator function of the OpenManipulator class.
void OpenManipulator::initOpenManipulator(bool using_actual_robot_state, STRING usb_port, STRING baud_rate, float control_loop_time)
{
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Manipulator Parameter
*****************************************************************************/
addWorld("world", // world name
"joint1"); // child name
addJoint("joint1", // my name
"world", // parent name
"joint2", // child name
math::vector3(0.012, 0.0, 0.017), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Z_AXIS, // axis of rotation
11, // actuator id
M_PI, // max joint limit (3.14 rad)
-M_PI, // min joint limit (-3.14 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
9.8406837e-02, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(3.4543422e-05, -1.6031095e-08, -3.8375155e-07,
3.2689329e-05, 2.8511935e-08,
1.8850320e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(-3.0184870e-04, 5.4043684e-04, 0.018 + 2.9433464e-02) // COM
);
addJoint("joint2", // my name
"joint1", // parent name
"joint3", // child name
math::vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0595), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Y_AXIS, // axis of rotation
12, // actuator id
M_PI_2, // max joint limit (1.67 rad)
-2.05, // min joint limit (-2.05 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
1.3850917e-01, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(3.3055381e-04, 9.7940978e-08, -3.8505711e-05,
3.4290447e-04, -1.5717516e-06,
6.0346498e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(1.0308393e-02, 3.7743363e-04, 1.0170197e-01) // COM
);
addJoint("joint3", // my name
"joint2", // parent name
"joint4", // child name
math::vector3(0.024, 0.0, 0.128), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Y_AXIS, // axis of rotation
13, // actuator id
1.53, // max joint limit (1.53 rad)
-M_PI_2, // min joint limit (-1.67 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
1.3274562e-01, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(3.0654178e-05, -1.2764155e-06, -2.6874417e-07,
2.4230292e-04, 1.1559550e-08,
2.5155057e-04), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(9.0909590e-02, 3.8929816e-04, 2.2413279e-04) // COM
);
addJoint("joint4", // my name
"joint3", // parent name
"gripper", // child name
math::vector3(0.124, 0.0, 0.0), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Y_AXIS, // axis of rotation
14, // actuator id
2.0, // max joint limit (2.0 rad)
-1.8, // min joint limit (-1.8 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
1.4327573e-01, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(8.0870749e-05, 0.0, -1.0157896e-06,
7.5980465e-05, 0.0,
9.3127351e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(4.4206755e-02, 3.6839985e-07, 8.9142216e-03) // COM
);
addTool("gripper", // my name
"joint4", // parent name
math::vector3(0.126, 0.0, 0.0), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
15, // actuator id
0.010, // max gripper limit (0.01 m)
-0.010, // min gripper limit (-0.01 m)
-0.015, // Change unit from `meter` to `radian`
3.2218127e-02 * 2, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(9.5568826e-06, 2.8424644e-06, -3.2829197e-10,
2.2552871e-05, -3.1463634e-10,
1.7605306e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(0.028 + 8.3720668e-03, 0.0246, -4.2836895e-07) // COM
);
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Kinematics
*****************************************************************************/
kinematics_ = new kinematics::SolverCustomizedforOMChain();
addKinematics(kinematics_);
if(using_actual_robot_state)
{
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Joint Actuator
*****************************************************************************/
actuator_ = new dynamixel::JointDynamixel();
// Set communication arguments
STRING dxl_comm_arg[2] = {usb_port, baud_rate};
void *p_dxl_comm_arg = &dxl_comm_arg;
// Set joint actuator id
std::vector<uint8_t> jointDxlId;
jointDxlId.push_back(11);
jointDxlId.push_back(12);
jointDxlId.push_back(13);
jointDxlId.push_back(14);
addJointActuator(JOINT_DYNAMIXEL, actuator_, jointDxlId, p_dxl_comm_arg);
// Set joint actuator control mode
STRING joint_dxl_mode_arg = "position_mode";
void *p_joint_dxl_mode_arg = &joint_dxl_mode_arg;
setJointActuatorMode(JOINT_DYNAMIXEL, jointDxlId, p_joint_dxl_mode_arg);
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Tool Actuator
*****************************************************************************/
tool_ = new dynamixel::GripperDynamixel();
uint8_t gripperDxlId = 15;
addToolActuator(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, tool_, gripperDxlId, p_dxl_comm_arg);
// Set gripper actuator control mode
STRING gripper_dxl_mode_arg = "current_based_position_mode";
void *p_gripper_dxl_mode_arg = &gripper_dxl_mode_arg;
setToolActuatorMode(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, p_gripper_dxl_mode_arg);
// Set gripper actuator parameter
STRING gripper_dxl_opt_arg[2];
void *p_gripper_dxl_opt_arg = &gripper_dxl_opt_arg;
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[0] = "Profile_Acceleration";
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[1] = "20";
setToolActuatorMode(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, p_gripper_dxl_opt_arg);
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[0] = "Profile_Velocity";
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[1] = "200";
setToolActuatorMode(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, p_gripper_dxl_opt_arg);
// Enable All Actuators
enableAllActuator();
// Receive current angles from all actuators
receiveAllJointActuatorValue();
receiveAllToolActuatorValue();
}
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Custom Trajectory
*****************************************************************************/
custom_trajectory_[0] = new custom_trajectory::Line();
custom_trajectory_[1] = new custom_trajectory::Circle();
custom_trajectory_[2] = new custom_trajectory::Rhombus();
custom_trajectory_[3] = new custom_trajectory::Heart();
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_LINE, custom_trajectory_[0]);
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_CIRCLE, custom_trajectory_[1]);
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_RHOMBUS, custom_trajectory_[2]);
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_HEART, custom_trajectory_[3]);
}
Set Robot Parameter
In the robotis_manipulator, the manipulator consists of world, joint components, and tool components, as shown below. world means the base where the manipulator is fixed. Joint components and tool components have a frame and a coordinates, respectively. In the case of the joint component, the coordinates is located on the rotation axis of the joint, and in the case of the tool component, the coordinates is the tool center position (TCP).
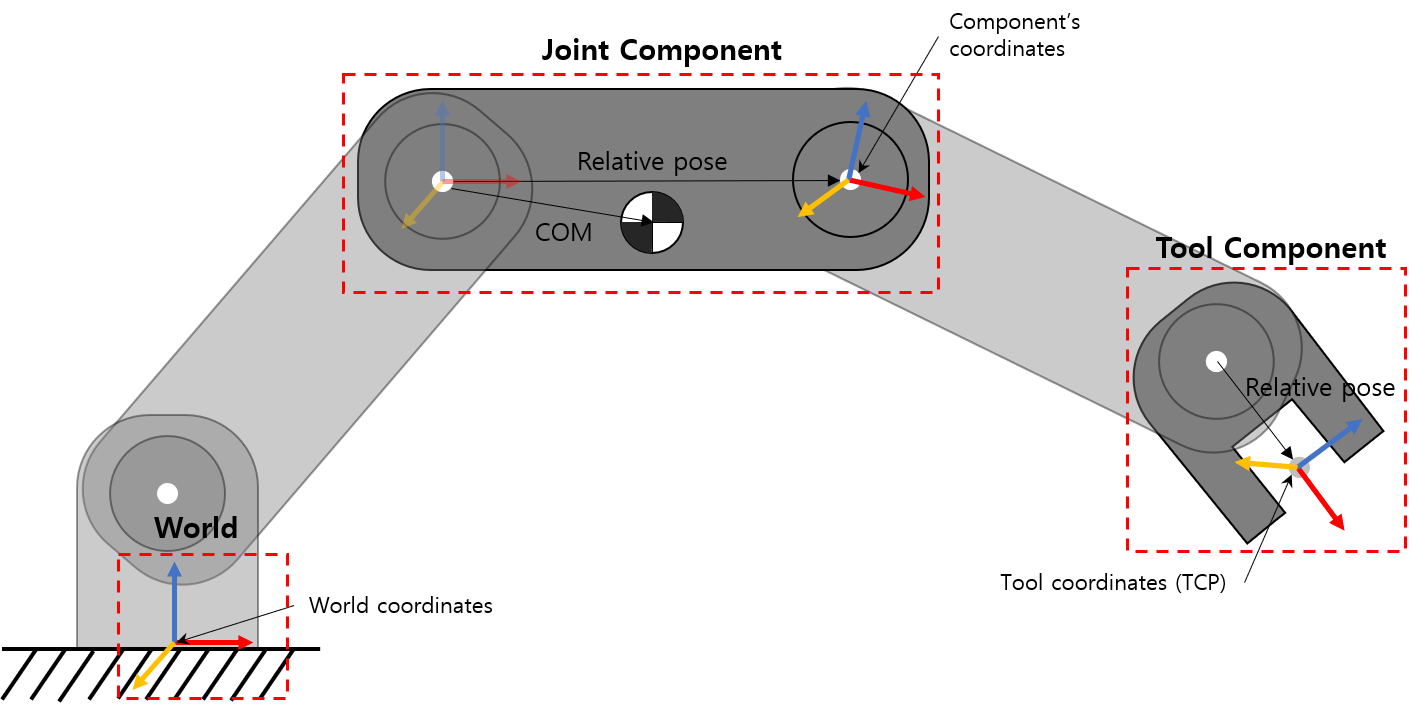
In the InitOpenManipulator function, the DH parameters of the manipulator are set as shown below.
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Manipulator Parameter
*****************************************************************************/
addWorld("world", // world name
"joint1"); // child name
addJoint("joint1", // my name
"world", // parent name
"joint2", // child name
math::vector3(0.012, 0.0, 0.017), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Z_AXIS, // axis of rotation
11, // actuator id
M_PI, // max joint limit (3.14 rad)
-M_PI, // min joint limit (-3.14 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
9.8406837e-02, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(3.4543422e-05, -1.6031095e-08, -3.8375155e-07,
3.2689329e-05, 2.8511935e-08,
1.8850320e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(-3.0184870e-04, 5.4043684e-04, 0.018 + 2.9433464e-02) // COM
);
addJoint("joint2", // my name
"joint1", // parent name
"joint3", // child name
math::vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0595), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Y_AXIS, // axis of rotation
12, // actuator id
M_PI_2, // max joint limit (1.67 rad)
-2.05, // min joint limit (-2.05 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
1.3850917e-01, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(3.3055381e-04, 9.7940978e-08, -3.8505711e-05,
3.4290447e-04, -1.5717516e-06,
6.0346498e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(1.0308393e-02, 3.7743363e-04, 1.0170197e-01) // COM
);
addJoint("joint3", // my name
"joint2", // parent name
"joint4", // child name
math::vector3(0.024, 0.0, 0.128), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Y_AXIS, // axis of rotation
13, // actuator id
1.53, // max joint limit (1.53 rad)
-M_PI_2, // min joint limit (-1.67 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
1.3274562e-01, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(3.0654178e-05, -1.2764155e-06, -2.6874417e-07,
2.4230292e-04, 1.1559550e-08,
2.5155057e-04), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(9.0909590e-02, 3.8929816e-04, 2.2413279e-04) // COM
);
addJoint("joint4", // my name
"joint3", // parent name
"gripper", // child name
math::vector3(0.124, 0.0, 0.0), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
Y_AXIS, // axis of rotation
14, // actuator id
2.0, // max joint limit (2.0 rad)
-1.8, // min joint limit (-1.8 rad)
1.0, // coefficient
1.4327573e-01, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(8.0870749e-05, 0.0, -1.0157896e-06,
7.5980465e-05, 0.0,
9.3127351e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(4.4206755e-02, 3.6839985e-07, 8.9142216e-03) // COM
);
addTool("gripper", // my name
"joint4", // parent name
math::vector3(0.126, 0.0, 0.0), // relative position
math::convertRPYToRotationMatrix(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), // relative orientation
15, // actuator id
0.010, // max gripper limit (0.01 m)
-0.010, // min gripper limit (-0.01 m)
-0.015, // Change unit from `meter` to `radian`
3.2218127e-02 * 2, // mass
math::inertiaMatrix(9.5568826e-06, 2.8424644e-06, -3.2829197e-10,
2.2552871e-05, -3.1463634e-10,
1.7605306e-05), // inertial tensor
math::vector3(0.028 + 8.3720668e-03, 0.0246, -4.2836895e-07) // COM
);
To set the DH parameters of the manipulator, use the addWorld, addJoint, addTool, and addComponentChild functions.
addWorld
void RobotisManipulator::addWorld(Name world_name,
Name child_name,
Eigen::Vector3d world_position = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero(),
Eigen::Matrix3d world_orientation = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity());
Sets a world in which the manipulator is fixed. The world refers to a base coordinates point where the manipulator is fixed, and this point can change depending on the state of the manipulator being fixed. One manipulator has only one world coordinates point.
- world_name : Specifies the name of world.
- child_name : Sets the next component name connected with world.
- world_position : Specifies the position of the initial world coordinates. it has a vector format, the default value is the origin of (0.0, 0.0, 0.0).
- world_orientation : Specifies the orientation of the initial world coordinates. it has a rotation matrix format, the default value is the Unit matrix.
addJoint
void RobotisManipulator::addJoint(Name my_name,
Name parent_name,
Name child_name,
Eigen::Vector3d relative_position,
Eigen::Matrix3d relative_orientation,
Eigen::Vector3d axis_of_rotation = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero(),
int8_t joint_actuator_id = -1,
double max_position_limit = M_PI,
double min_position_limit = -M_PI,
double coefficient = 1.0,
double mass = 0.0,
Eigen::Matrix3d inertia_tensor = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity(),
Eigen::Vector3d center_of_mass = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero());
Add a joint component of the manipulator. The Joint component refers to the components of all joints that run with or without an actuator. The end-effectors located at the end of the manipulator are excluded from the joint component. The position and orientation of the joint component refers to the position and orientation of the rotation axis coordinates where the joint is located.
- my_name : Specifies the name of the corresponding joint component.
- parent_name : Specifies the name of a previous component to which this joint component is linked.
- child_name : Specifies the name of a next component to which this joint component is linked.
- relative_position : Specifies the relative position of the joint coordinates from the coordinates of the parent component in a vector format.
- relative_orientation : Specifies the relative orientation of the joint coordinates from the coordinates of the parent component in a rotation matrix format.
- axis_of_rotation : Specify the rotation axis of the joint component. The rotation axis is in the coordinates set by relative_position and relative_orientation.
- joint_actuator_id : Specifies the id of the actuator used for this joint. id can be set to a natural number greater than or equal to 0, and can not be used redundantly on plural joints. If id is set to -1, the joint is specified as a passive joint with no actuator attached.
- max_position_limit : Specifies the upper bound of the movable range of the joint.
- min_position_limit : Specifies the lower bound of the movable range for the joint.
- coefficient : Specify the reduction ratio by the structure of the joint. This value represents the ratio of the position value of the actuator to the position value of the joint.
- mass : Specifies the mass of the joint component.
- inertia_tensor : Specifies the inertia tensor of the joint component. This value is defined for the parent component coordinates.
- center_of_mass : Specifies the center of mass of the joint component. This value is defined for the parent component coordinates.
addTool
void RobotisManipulator::addTool(Name my_name,
Name parent_name,
Eigen::Vector3d relative_position,
Eigen::Matrix3d relative_orientation,
int8_t tool_id = -1,
double max_position_limit =M_PI,
double min_position_limit = -M_PI,
double coefficient = 1.0,
double mass = 0.0,
Eigen::Matrix3d inertia_tensor = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity(),
Eigen::Vector3d center_of_mass = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero());
Add a tool component of the manipulator. The tool, called the end-effectors of the manipulator, is mounted at the end of the manipulator, it hasn’t any child component. A manipulator can be configured to have plural tools.
- my_name : Specifies the name of the corresponding tool component.
- parent_name : Specifies the name of a previous component to which this tool component is linked.
- relative_position : Specifies the relative position of the tool coordinates from the coordinates of the parent component in a vector format.
- relative_orientation : Specifies the relative orientation of the joint coordinates from the coordinates of the parent component in a rotation matrix format.
- tool_id : Specifies the id of the actuator used in the tool. id can be set to a natural number greater than or equal to 0, and can not be used redundantly with plural components. If id is set to -1, the tool is specified as a passive end-effector with no actuator attached.
- max_position_limit : Specifies the upper end of the end-effector’s run range.
- min_position_limit : Specifies the lower end of the end-effector’s run range.
- coefficient : Indicates the ratio of the position value of the actuator to the position value of the tool.
- mass : Specifies the mass of the tool component.
- inertia_tensor : Specifies the inertia tensor of the tool component. This value is defined for the parent component coordinates.
- center_of_mass : Specifies the center of mass of the tool component. This value is defined for the parent component coordinates.
addComponentChild
void RobotisManipulator::addComponentChild(Name my_name, Name child_name);
After the addJoint function, add the child component of the component using the addComponentChild function. Used when the joint component has child components other than the child_name already specified in the addJoint function. The tool component does not have child components because it is located at the end of the manipulator.
- my_name : Specifies the name of the joint.
- child_name : Specifies the name of a child component to add.
Add Kinematics Object
In the initOpenManipulator function, the kinematics solving algorithm used to control the manipulator is added as shown below.
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Kinematics
*****************************************************************************/
kinematics_ = new kinematics::SolverCustomizedforOMChain();
addKinematics(kinematics_);
The kinematics solving algorism depends on the user’s manipulator. Therefore, robotis_manipulator is configured so that the user can configure the kinematics solver and test his algorithm. Of course, about the general purpose solving algorithm for the serial linkage structure manipulators, the following kinematics solver class is provided in open_manipulator_libs.
- Kinematics Solver Using Chain Rule and Jacobian
- Kinematics Solver Using Chain Rule and Singularity Robust Jacobian
- Kinematics Solver Using Chain Rule and Singularity Robust Position Only Jacobian
If the user wants to apply his algorithm to own manipulator, user can create a new kinematics solver class. This new class is created by inheriting the robotis_manipulator::kinematics class below.
robotis_manipulator::kinematicsclass Kinematics { public: Kinematics() {} virtual ~Kinematics() {} virtual void setOption(const void *arg) = 0; virtual Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian(Manipulator *manipulator, Name tool_name) = 0; virtual void solveForwardKinematics(Manipulator *manipulator) = 0; virtual bool solveInverseKinematics(Manipulator *manipulator, Name tool_name, Pose target_pose, std::vector<JointValue>* goal_joint_position) = 0; };
The kinematics::SolverCustomizedforOMChain class used by OpenManipulator-X consists of the following.
/*****************************************************************************
** Kinematics Solver Customized for OpenManipulator Chain
*****************************************************************************/
class SolverCustomizedforOMChain : public robotis_manipulator::Kinematics
{
private:
void forwardSolverUsingChainRule(Manipulator *manipulator, Name component_name);
bool chainCustomInverseKinematics(Manipulator *manipulator, Name tool_name, Pose target_pose, std::vector<JointValue>* goal_joint_value);
public:
SolverCustomizedforOMChain(){}
virtual ~SolverCustomizedforOMChain(){}
virtual void setOption(const void *arg);
virtual MatrixXd jacobian(Manipulator *manipulator, Name tool_name);
virtual void solveForwardKinematics(Manipulator *manipulator);
virtual bool solveInverseKinematics(Manipulator *manipulator, Name tool_name, Pose target_pose, std::vector<JointValue>* goal_joint_value);
};
In order to use all API functions of robotis_manipulator, the following every functions declared as virtual must be written such as in the above kinematics::SolverCustomizedforOMChain class.
Configure each virtual function to do the following:
- setOption :
When need to change the kinematics solver option, configure to set the option (class member parameter) by using the
argpointer parameter. - jacobian :
Configure to return the
MatrixXdjacobian matrix for the pose of a specific component setted thenametool_name, using the parameters (joint_value, relative, joint_constant, etc.) of the component parameters of theManipulatormanipulator. - solveForwardKinematics :
Configure to solve the forward kinematics of the manipulator using the parameters (joint_value, relative, joint_constant, etc.) of the components of the
Manipulatormanipulator and return by setting thePosepose_from_world values of each component parameter. - solveInverseKinematics :
Configure to return
std::vector<JointValue>*goal_joint_value by solving the inverse kinematics for positionning thePosepose_from_world of thenametool_name component toPosetarget_pose.
Add Actuator Object
In the initOpenManipulator function, the actuator classes to be used to control actuators of the manipulator is added as shown below.
if(using_actual_robot_state)
{
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Joint Actuator
*****************************************************************************/
actuator_ = new dynamixel::JointDynamixel();
// Set communication arguments
STRING dxl_comm_arg[2] = {usb_port, baud_rate};
void *p_dxl_comm_arg = &dxl_comm_arg;
// Set joint actuator id
std::vector<uint8_t> jointDxlId;
jointDxlId.push_back(11);
jointDxlId.push_back(12);
jointDxlId.push_back(13);
jointDxlId.push_back(14);
addJointActuator(JOINT_DYNAMIXEL, actuator_, jointDxlId, p_dxl_comm_arg);
// Set joint actuator control mode
STRING joint_dxl_mode_arg = "position_mode";
void *p_joint_dxl_mode_arg = &joint_dxl_mode_arg;
setJointActuatorMode(JOINT_DYNAMIXEL, jointDxlId, p_joint_dxl_mode_arg);
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Tool Actuator
*****************************************************************************/
tool_ = new dynamixel::GripperDynamixel();
uint8_t gripperDxlId = 15;
addToolActuator(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, tool_, gripperDxlId, p_dxl_comm_arg);
// Set gripper actuator control mode
STRING gripper_dxl_mode_arg = "current_based_position_mode";
void *p_gripper_dxl_mode_arg = &gripper_dxl_mode_arg;
setToolActuatorMode(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, p_gripper_dxl_mode_arg);
// Set gripper actuator parameter
STRING gripper_dxl_opt_arg[2];
void *p_gripper_dxl_opt_arg = &gripper_dxl_opt_arg;
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[0] = "Profile_Acceleration";
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[1] = "20";
setToolActuatorMode(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, p_gripper_dxl_opt_arg);
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[0] = "Profile_Velocity";
gripper_dxl_opt_arg[1] = "200";
setToolActuatorMode(TOOL_DYNAMIXEL, p_gripper_dxl_opt_arg);
// Enable All Actuators
enableAllActuator();
// Receive current angles from all actuators
receiveAllJointActuatorValue();
receiveAllToolActuatorValue();
}
The actuator class for joints were added using the addJointActuator function, and the actuator class for a tool were added using the addToolActuator function.
The control mode settings for both classes were set using setJointActuatorMode and setToolActuatorMode functions.
The JointDynamixel and GripperDynamixel classes can be used with DYNAMIXEL, otherwise the user will need to create the JointActuator and the ToolActuator for own actuator.
Plural JointActuator and ToolActuator classes can be added when various kinds of actuators is used in one manipulator.
Joint Actuator Class
The newly created joint actuator class is created by inheriting the following robotis_manipulator::JointActuator class.
robotis_manipulator::JointActuator
class JointActuator
{
public:
bool enabled_state_;
JointActuator() : enabled_state_(false) {}
virtual ~JointActuator() {}
virtual void init(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, const void *arg) = 0;
virtual void setMode(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, const void *arg) = 0;
virtual std::vector<uint8_t> getId() = 0;
virtual void enable() = 0;
virtual void disable() = 0;
virtual bool sendJointActuatorValue(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, std::vector<ActuatorValue> value_vector) = 0;
virtual std::vector<ActuatorValue> receiveJointActuatorValue(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id) = 0;
bool findId(uint8_t actuator_id);
bool getEnabledState();
};
The JointDynamixel class used by OpenManipulator has the following structure.
class JointDynamixel : public robotis_manipulator::JointActuator
{
private:
DynamixelWorkbench *dynamixel_workbench_;
Joint dynamixel_;
std::vector<AccelerationCalculator> acceleration_calculator_;
std::vector<LowPassFilter> velocity_filter_;
double previous_time_;
public:
JointDynamixel();
virtual ~JointDynamixel(){}
/*****************************************************************************
** Joint Dynamixel Control Functions
*****************************************************************************/
virtual void init(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, const void *arg);
virtual void setMode(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, const void *arg);
virtual std::vector<uint8_t> getId();
virtual void enable();
virtual void disable();
virtual bool sendJointActuatorValue(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, std::vector<robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValue> value_vector);
virtual std::vector<robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValue> receiveJointActuatorValue(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id);
/*****************************************************************************
** Functions called in Joint Dynamixel Control Functions
*****************************************************************************/
bool initialize(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, STRING dxl_device_name, STRING dxl_baud_rate);
bool setOperatingMode(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, STRING dynamixel_mode = "position_mode");
bool setSDKHandler(uint8_t actuator_id);
bool writeProfileValue(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, STRING profile_mode, uint32_t value);
bool writeGoalPosition(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id, std::vector<double> radian_vector);
std::vector<robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValue> receiveAllDynamixelValue(std::vector<uint8_t> actuator_id);
};
In order to use all API functions of robotis_manipulator, the following every virtual functions must be written such as in the above JointDynamixel class.
Configure each virtual function to do the following:
- init :
Configure the function to set the
std::vector<uint8_t>actuator_id of the actuator to be used in this class and to be able to set the other required setting parameters usingconst void*arg. The value ofactuator_idis the same as the value set in Set Robot Parameter. - setMode :
Set the mode of the actuators setted to
std::vector<uint8_t>actuator_id to the value ofconst void*arg. Depending on the type of actuator, it may not be necessary. - getId :
Configure to returns the
std::vector<uint8_t>actuator_id set by theinitfunction. If severalJointAcuatorclasses are added, they are used to determine the id of the actuator contained in this object. - enable :
It is used to enable the actuators controlled by this class. To getting the enabled state by the
getEnabledStatefunction, set member parameter enabled_state_ to true in this function. -
disable : It is used to disable the actuators controlled by this class. If actuator is disabled, the actuated will not move even if
sendJointActuatorValueis executed. To getting the enabled state by thegetEnabledStatefunction, set member parameter enabled_state_ to false in this function. -
sendJointActuatorValue : Configure the function the
std::vector<uint8_t>actuator_id actuators move tostd::vector<robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValue>value_vector, when the function is executed. In this case, value_vector is notJointValueof the joint butActuatorValuewhich does not go through the decelerator. value_vector contains position, velocity, acceleration, and effort for each actuator. Depending on the actuator, it is also possible to fill only the position values and leave the remaining values empty. - receiveJointActuatorValue :
Configure to receive the
std::vector<robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValue>present actuator values of the actuators.ActuatorValueincludes* position, *velocity, acceleration, and effort of each actuator. This values are stored in the manipulator parameters after the values are multiplied by the coefficient value set in Set Robot Parameter. In the other word, it is notJointValuebutActuatorValuewhich does not go through decelerator. Depending on the actuator, it is possible to fill only the position value and leave the rest of the value blank, but it can be used to calculate the dynamic.pose value of each component by returning with velocity and acceleration.
Tool Actuator Class
The newly created tool actuator class is created by inheriting the following robotis_manipulator::ToolActuator class.
robotis_manipulator::ToolActuator
class ToolActuator
{
public:
bool enabled_state_;
ToolActuator():enabled_state_(false){}
virtual ~ToolActuator() {}
virtual void init(uint8_t actuator_id, const void *arg) = 0;
virtual void setMode(const void *arg) = 0;
virtual uint8_t getId() = 0;
virtual void enable() = 0;
virtual void disable() = 0;
virtual bool sendToolActuatorValue(ActuatorValue value) = 0;
virtual ActuatorValue receiveToolActuatorValue() = 0;
bool findId(uint8_t actuator_id);
bool getEnabledState();
};
The GripperDynamixel class used by OpenManipulator has the following structure.
class GripperDynamixel : public robotis_manipulator::ToolActuator
{
private:
DynamixelWorkbench *dynamixel_workbench_;
Joint dynamixel_;
public:
GripperDynamixel() {}
virtual ~GripperDynamixel() {}
/*****************************************************************************
** Tool Dynamixel Control Functions
*****************************************************************************/
virtual void init(uint8_t actuator_id, const void *arg);
virtual void setMode(const void *arg);
virtual uint8_t getId();
virtual void enable();
virtual void disable();
virtual bool sendToolActuatorValue(robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValue value);
virtual robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValue receiveToolActuatorValue();
/*****************************************************************************
** Functions called in Tool Dynamixel Profile Control Functions
*****************************************************************************/
bool initialize(uint8_t actuator_id, STRING dxl_device_name, STRING dxl_baud_rate);
bool setOperatingMode(STRING dynamixel_mode = "position_mode");
bool writeProfileValue(STRING profile_mode, uint32_t value);
bool setSDKHandler();
bool writeGoalPosition(double radian);
double receiveDynamixelValue();
};
In order to use all API functions of robotis_manipulator, the following every virtual functions must be written such as in the above GripperDynamixel class.
Configure each virtual function to do the following:
- init :
Configure the function to set the
uint8_tactuator_id of the actuator to be used in this class and to be able to set the other required setting parameters usingconst void*arg. The value ofactuator_idis the same as the value set in Set Robot Parameter. A singleToolActuatorclass controls only one tool actuator. If you set up more than one tool on the manipulator, create anotherToolActuatorclass and add it through theaddToolActuatorfunction. - setMode :
Set the mode of the actuators setted to
uint8_tactuator_id to the value ofconst void*arg. Depending on the type of actuator, it may not be necessary. - getId :
Configure to returns the
uint8_tactuator_id set by theinitfunction. If severalToolAcuatorclasses are added, they are used to determine the id of the actuator contained in this object. - enable :
It is used to enable the actuator controlled by this class. To getting the enabled state by the
getEnabledStatefunction, set member parameter enabled_state_ to true in this function. - disable :
It is used to disable the actuator controlled by this class. If actuator is disabled, the actuated will not move even if
sendToolActuatorValueis executed. To getting the enabled state by thegetEnabledStatefunction, set member parameter enabled_state_ to false in this function. - sendToolActuatorValue
Configure the function the
uint8_tactuator_id actuator move torobotis_manipulator::ActuatorValuevalue, when the function is executed. In this case, value is notToolValueof the tool butActuatorValuewhich does not go through the decelerator. value contains position, velocity, acceleration, and effort for the actuator. Depending on the actuator, it is also possible to fill only the position values and leave the remaining values empty. - receiveToolActuatorValue
Configure to receive the
robotis_manipulator::ActuatorValuepresent actuator value of the tool actuator.ActuatorValueincludes* position, *velocity, acceleration, and effort of the actuator. This values are stored in the manipulator parameters after the values are multiplied by the coefficient value set in Set Robot Parameter. In the other word, it is notToolValuebutActuatorValuewhich does not go through decelerator. Depending on the actuator, it is possible to fill only the position value and leave the rest of the value blank, but it can be used to calculate the dynamic.pose value of each component by returning with velocity and acceleration.
Add Custom Trajectory Object
Even if you do not add this trajectory generator class, you can create a basic trajectory (TCP, joint) using a minimum jerk, but you need to add a custom_trajectory class to make the manipulator move along your own trajectory.
In the initOpenManipulator function, add custom_trajectory to be used to create the manipulator’s path (trajectory) as shown below.
/*****************************************************************************
** Initialize Custom Trajectory
*****************************************************************************/
custom_trajectory_[0] = new custom_trajectory::Line();
custom_trajectory_[1] = new custom_trajectory::Circle();
custom_trajectory_[2] = new custom_trajectory::Rhombus();
custom_trajectory_[3] = new custom_trajectory::Heart();
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_LINE, custom_trajectory_[0]);
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_CIRCLE, custom_trajectory_[1]);
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_RHOMBUS, custom_trajectory_[2]);
addCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_HEART, custom_trajectory_[3]);
The custom trajectory class is added through the addCustomTrajectory function, and it has kinds of the CustomJointTrajectory class that returns the JointWaypoint as the path value and the CustomTaskTrajectory class that returns the TaskWaypoint as the path value. Each of these classes is created by inheriting the following robotis_manipulator::CustomJointTrajectory and robotis_manipulator::CustomTaskTrajectory classes.
robotis_manipulator::CustomJointTrajectory
class CustomJointTrajectory
{
public:
CustomJointTrajectory() {}
virtual ~CustomJointTrajectory() {}
virtual void makeJointTrajectory(double move_time, JointWaypoint start, const void *arg) = 0;
virtual void setOption(const void *arg) = 0;
virtual JointWaypoint getJointWaypoint(double tick) = 0;
};
robotis_manipulator::CustomTaskTrajectory
class CustomTaskTrajectory
{
public:
CustomTaskTrajectory() {}
virtual ~CustomTaskTrajectory() {}
virtual void makeTaskTrajectory(double move_time, TaskWaypoint start, const void *arg) = 0;
virtual void setOption(const void *arg) = 0;
virtual TaskWaypoint getTaskWaypoint(double tick) = 0;
};
When you create a class that inherits from the above classes, you must write the following virtual functions to use the trajectory added through the API function of robotis_manipulator.
Configure each virtual function to do the following:
- makeJointTrajectory, makeTaskTrajectory :
When this function is executed, create and save a trajectory expression that can be reached in
doublemove_time from start to arg (free form) as the class member variable. When thegetJointWaypointorgetTaskWaypointfunction is executed, it should returnJointWaypointor ` TaskWaypointaccording to thedouble` tick time (difference from the start time to the present time). - setOption : Configure this function to use for setting some option data to create the path (trajectory) by using arg.
- getJointWaypoint, getTaskWaypoint :
Configure this function to return the trajectory generated by
makeJointTrajectoryormakeTaskTrajectoryasJointWaypointorTaskWaypointabout the tick time (difference from the start time to the present time) .
The Circle trajectory class used in OpenManipulator-X is structured as follows.
/*****************************************************************************
** Circle
*****************************************************************************/
class Circle : public robotis_manipulator::CustomTaskTrajectory
{
private:
robotis_manipulator::MinimumJerk path_generator_;
VectorXd coefficient_;
TaskWaypoint start_pose_;
TaskWaypoint goal_pose_;
double radius_;
double start_angular_position_;
double revolution_;
public:
Circle() {}
virtual ~Circle() {}
void initCircle(double move_time, TaskWaypoint start, double radius, double revolution, double start_angular_position);
TaskWaypoint drawCircle(double time_var);
virtual void setOption(const void *arg);
virtual void makeTaskTrajectory(double move_time, TaskWaypoint start, const void *arg);
virtual TaskWaypoint getTaskWaypoint(double tick);
};
Step3 Make Control process Function
Make the manipulator a function of the control process. Although it is possible to write directly from a controller package, it is useful to create a controller package that controls several identical manipulators by pre-populating the process to be used primarily.
In OpenManipulator-X, the process functions are configured as follows.
void OpenManipulator::processOpenManipulator(double present_time)
{
JointWaypoint goal_joint_value = getJointGoalValueFromTrajectory(present_time);
JointWaypoint goal_tool_value = getToolGoalValue();
receiveAllJointActuatorValue();
receiveAllToolActuatorValue();
if(goal_joint_value.size() != 0) sendAllJointActuatorValue(goal_joint_value);
if(goal_tool_value.size() != 0) sendAllToolActuatorValue(goal_tool_value);
solveForwardKinematics();
}
- The
goal_joint_valueandgoal_tool_valuevalues are returned from the trajectory calculated by the make trajectory functions throughgetJointGoalValueFromTrajectoryandgetToolGoalValue. If you used themakeTaskTrajectoryfunction, the inverse kinematics is solved inside of thegetJointGoalValueFromTrajectoryfunction. - present joint values and tool value are returned through the
receiveAllJointActuatorValueandreceiveAllToolActuatorValue. These values are stored in themanipulator_member variable of theRobotisManipulatorclass. - Send the
goal_joint_valueandgoal_tool_valuevalues got fromgetJointGoalValueFromTrajectoryandgetToolGoalValueto the actuator controller throughsendAllJointActuatorValueandsendAllToolActuatorValuefunctions. This will move the actuator to reach the target position. - Solve the forward kinematics based on the present joint values received through
receiveAllJointActuatorValue,receiveAllToolActuatorValueand stored the pose value of components calculated to the manipulator_.
Step4 Use it
Configure the controller package for the manipulator using the classes and functions you created above. For APIs available on the controller, see here. For example, the controller package of OpenManipulator-X running on OpenCR is composed as follows.
open_manipulator_chain.ino
#include <open_manipulator_libs.h>
#include "processing.h"
#include "remote_controller.h"
OpenManipulator open_manipulator;
double control_time = 0.010;
double present_time = 0.0;
double previous_time = 0.0;
bool platform_state = true;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(57600);
DEBUG.begin(57600);
// while (!Serial)
// ;
connectProcessing(platform_state);
connectRC100();
open_manipulator.initOpenManipulator(platform_state);
log::println("OpenManipulator Debugging Port");
}
void loop()
{
present_time = millis()/1000.0;
getData(100);
playProcessingMotion(&open_manipulator);
if(present_time-previous_time >= control_time)
{
open_manipulator.processOpenManipulator(millis()/1000.0);
previous_time = millis()/1000.0;
sendValueToProcessing(&open_manipulator);
}
}
void getData(uint32_t wait_time)
{
static uint8_t state = 0;
static uint32_t tick = 0;
bool rc100_state = false;
bool processing_state = false;
uint16_t get_rc100_data = 0;
String get_processing_data = "";
if (availableRC100())
{
get_rc100_data = readRC100Data();
rc100_state = true;
}
if (availableProcessing())
{
get_processing_data = readProcessingData();
processing_state = true;
}
switch (state)
{
case 0:
if (rc100_state)
{
fromRC100(&open_manipulator, get_rc100_data);
tick = millis();
state = 1;
}
else if (processing_state)
{
fromProcessing(&open_manipulator, get_processing_data);
tick = millis();
state = 1;
}
break;
case 1:
if ((millis() - tick) >= wait_time)
{
state = 0;
}
break;
default:
state = 0;
break;
}
}
processing.h
#include <open_manipulator_libs.h>
#define DXL_SIZE 5
typedef struct _MotionWaypoint
{
std::vector<double> angle;
double path_time;
double gripper_value;
} MotionWaypoint;
std::vector<MotionWaypoint> motion_way_point_buf;
bool processing_motion_state = false;
char hand_motion_cnt = 0;
bool hand_motion_repeat_state = false;
bool platform_state_processing = false;
String global_cmd[50];
void connectProcessing(bool platform)
{
platform_state_processing = platform;
for (int i = 0; i < DXL_SIZE; i++)
{
Serial.print(0.0);
Serial.print(",");
}
Serial.println(0.0);
delay(300);
Serial.println("Init Processing");
}
int availableProcessing()
{
return Serial.available();
}
String readProcessingData()
{
return Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
}
void split(String data, char separator, String* temp)
{
int cnt = 0;
int get_index = 0;
String copy = data;
while(true)
{
get_index = copy.indexOf(separator);
if(-1 != get_index)
{
temp[cnt] = copy.substring(0, get_index);
copy = copy.substring(get_index + 1);
}
else
{
temp[cnt] = copy.substring(0, copy.length());
break;
}
++cnt;
}
}
String* parseDataFromProcessing(String get)
{
get.trim();
split(get, ',', global_cmd);
return global_cmd;
}
void sendAngleToProcessing(JointWaypoint joint_states_vector)
{
Serial.print("angle");
for (int i = 0; i < (int)joint_states_vector.size(); i++)
{
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(joint_states_vector.at(i).position, 3);
}
Serial.print("\n");
}
void sendToolDataToProcessing(ToolValue value)
{
Serial.print("tool");
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(value.position * 10);
Serial.print("\n");
}
void sendValueToProcessing(OpenManipulator *open_manipulator)
{
sendAngleToProcessing(open_manipulator->getAllActiveJointValue());
sendToolDataToProcessing(open_manipulator->getToolValue("gripper"));
}
void fromProcessing(OpenManipulator *open_manipulator, String data)
{
String *cmd = parseDataFromProcessing(data);
if (cmd[0] == "opm")
{
if (cmd[1] == "ready")
{
if(platform_state_processing)
{
open_manipulator->enableAllActuator();
sendValueToProcessing(open_manipulator);
}
}
else if (cmd[1] == "end")
{
if(platform_state_processing)
{
open_manipulator->disableAllActuator();
}
}
}
////////// joint space control tab
else if (cmd[0] == "joint")
{
std::vector<double> goal_position;
for (uint8_t index = 0; index < DXL_SIZE; index++)
{
goal_position.push_back((double)cmd[index + 1].toFloat());
}
open_manipulator->makeJointTrajectory(goal_position, 1.0); // FIX TIME PARAM
}
else if (cmd[0] == "gripper")
{
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", (double)cmd[1].toFloat());
}
else if (cmd[0] == "grip")
{
if (cmd[1] == "on")
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", -0.009);
else if (cmd[1] == "off")
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", 0.009);
}
////////// task space control tab
else if (cmd[0] == "task")
{
if (cmd[1] == "forward")
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.010, 0.0, 0.0), 0.2);
else if (cmd[1] == "back")
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(-0.010, 0.0, 0.0), 0.2);
else if (cmd[1] == "left")
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, 0.010, 0.0), 0.2);
else if (cmd[1] == "right")
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, -0.010, 0.0), 0.2);
else if (cmd[1] == "up")
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.010), 0.2);
else if (cmd[1] == "down")
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, 0.0, -0.010), 0.2);
else
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), 0.2);
}
else if (cmd[0] == "torque")
{
if(platform_state_processing)
{
if (cmd[1] == "on")
open_manipulator->enableAllJointActuator();
else if (cmd[1] == "off")
open_manipulator->disableAllJointActuator();
}
}
////////// hand teaching tab
else if (cmd[0] == "get")
{
if (cmd[1] == "clear") // motion clear
{
processing_motion_state = false;
motion_way_point_buf.clear();
hand_motion_cnt = 0;
}
else if (cmd[1] == "pose") // save pose
{
MotionWaypoint read_value;
JointWaypoint present_states = open_manipulator->getAllActiveJointValue();
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < present_states.size(); i ++)
read_value.angle.push_back(present_states.at(i).position);
read_value.path_time = 2.0; // FIX TIME PARAM
read_value.gripper_value = open_manipulator->getToolValue("gripper").position;
motion_way_point_buf.push_back(read_value);
hand_motion_cnt = 0;
}
else if (cmd[1] == "on") // save gripper on
{
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", -0.009);
}
else if (cmd[1] == "off") // save gripper off
{
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", 0.009);
}
}
else if (cmd[0] == "hand")
{
if (cmd[1] == "once") // play motion (once)
{
processing_motion_state = true;
}
else if (cmd[1] == "repeat") // play motion (repeat)
{
hand_motion_repeat_state = true;
}
else if (cmd[1] == "stop") // play motion (stop)
{
hand_motion_repeat_state = false;
processing_motion_state = false;
hand_motion_cnt = 0;
}
}
////////// motion tab
else if (cmd[0] == "motion")
{
if (cmd[1] == "1")
{
TaskWaypoint draw_line_arg;
draw_line_arg.kinematic.position(0) = 0.02;
draw_line_arg.kinematic.position(1) = 0.02;
draw_line_arg.kinematic.position(2) = -0.02;
void *p_draw_line_arg = &draw_line_arg;
open_manipulator->makeCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_LINE, "gripper", p_draw_line_arg, 1.0);
}
else if (cmd[1] == "2")
{
double draw_circle_arg[3];
draw_circle_arg[0] = 0.03; // radius (m)
draw_circle_arg[1] = 2; // revolution
draw_circle_arg[2] = 0.0; // start angle position (rad)
void* p_draw_circle_arg = &draw_circle_arg;
open_manipulator->makeCustomTrajectory(CUSTOM_TRAJECTORY_CIRCLE, "gripper", p_draw_circle_arg, 4.0);
}
}
}
void playProcessingMotion(OpenManipulator *open_manipulator)
{
if(!open_manipulator->getMovingState() && processing_motion_state)
{
if(motion_way_point_buf.size() == 0)
return;
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", motion_way_point_buf.at(hand_motion_cnt).gripper_value);
open_manipulator->makeJointTrajectory(motion_way_point_buf.at(hand_motion_cnt).angle, motion_way_point_buf.at(hand_motion_cnt).path_time);
hand_motion_cnt ++;
if(hand_motion_cnt >= motion_way_point_buf.size())
{
hand_motion_cnt = 0;
if(!hand_motion_repeat_state)
processing_motion_state = false;
}
}
}
remote_controller.h
#include <open_manipulator_libs.h>
#include <RC100.h>
RC100 rc100;
double grip_value = 0.0;
void connectRC100()
{
rc100.begin(1);
}
int availableRC100()
{
return rc100.available();
}
uint16_t readRC100Data()
{
return rc100.readData();
}
void fromRC100(OpenManipulator* open_manipulator, uint16_t data)
{
if (data & RC100_BTN_U)
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.007, 0.0, 0.0), 0.16);
else if (data & RC100_BTN_D)
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(-0.007, 0.0, 0.0), 0.16);
else if (data & RC100_BTN_L)
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, 0.007, 0.0), 0.16);
else if (data & RC100_BTN_R)
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, -0.007, 0.0), 0.16);
else if (data & RC100_BTN_1)
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.007), 0.16);
else if (data & RC100_BTN_3)
open_manipulator->makeTaskTrajectoryFromPresentPose("gripper", math::vector3(0.0, 0.0, -0.007), 0.16);
else if (data & RC100_BTN_2)
{
grip_value += 0.0020;
if (grip_value > 0.01f)
grip_value = 0.01f;
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", grip_value);
}
else if (data & RC100_BTN_4)
{
grip_value -= 0.002;
if (grip_value < -0.01f)
grip_value = -0.01f;
open_manipulator->makeToolTrajectory("gripper", grip_value);
}
else if (data & RC100_BTN_5)
{
std::vector<double> goal_position;
goal_position.push_back(0.0);
goal_position.push_back(-60.0 * DEG2RAD);
goal_position.push_back(20.0 * DEG2RAD);
goal_position.push_back(40.0 * DEG2RAD);
open_manipulator->makeJointTrajectory(goal_position, 1.5);
}
else if (data & RC100_BTN_6)
{
std::vector<double> goal_position;
goal_position.push_back(0.0);
goal_position.push_back(0.0);
goal_position.push_back(0.0);
goal_position.push_back(0.0);
open_manipulator->makeJointTrajectory(goal_position, 1.0);
}
}